Stroke
At Extivita, we believe integrative medicine plays a critical role in supporting overall health and addressing complex neurological conditions like a stroke. Our therapies are designed to complement conventional rehabilitation programs by targeting contributing factors such as inflammation, oxidative stress, impaired circulation, and poor nutrient absorption—factors that can significantly impact recovery, brain function, and quality of life during and after stroke recovery.
Our treatment offerings are grounded in clinical research and focus on holistic, personalized approaches that work alongside your medical care team. Extivita provides therapies such as Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), Neurofeedback Therapy, Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy, and Nutritional IV Therapy, all tailored to support the brain and body’s natural healing capacity, improve circulation, enhance neurological function, and reduce post-stroke complications. By supporting the body at the cellular level, these therapies help stroke patients regain strength, enhance function, and promote long-term wellness.
Understanding Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and essential nutrients. This can result from a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or a ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). Without prompt treatment, brain cells begin to die within minutes, leading to lasting neurological damage that can affect speech, movement, memory, and other critical functions.
Brain cells are highly sensitive to oxygen deprivation. When oxygen levels drop, energy production within neurons is disrupted, impairing communication between brain cells and, in some cases, causing permanent cell death. Poor circulation, chronic inflammation, and oxidative stress can worsen the initial damage and slow recovery.
Inflammation is a key factor in the brain’s response to stroke. While short-term inflammation supports the early stages of healing, prolonged or excessive inflammation can damage healthy brain tissue, disrupt the rebuilding of neural pathways, and hinder the brain’s natural repair processes.
The body’s detoxification systems—the liver, kidneys, lymphatic system, and skin—also influence neurological health. When these systems are overburdened by toxins, poor diet, or stress, oxidative stress within the brain can increase, creating an environment that is less supportive of recovery. Addressing these underlying factors is essential to restoring balance, supporting brain function, and promoting long-term healing after a stroke.
Extivita Therapies for Stroke Recovery

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy

Neurofeedback Therapy

Nutritional IV Therapy

Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF)
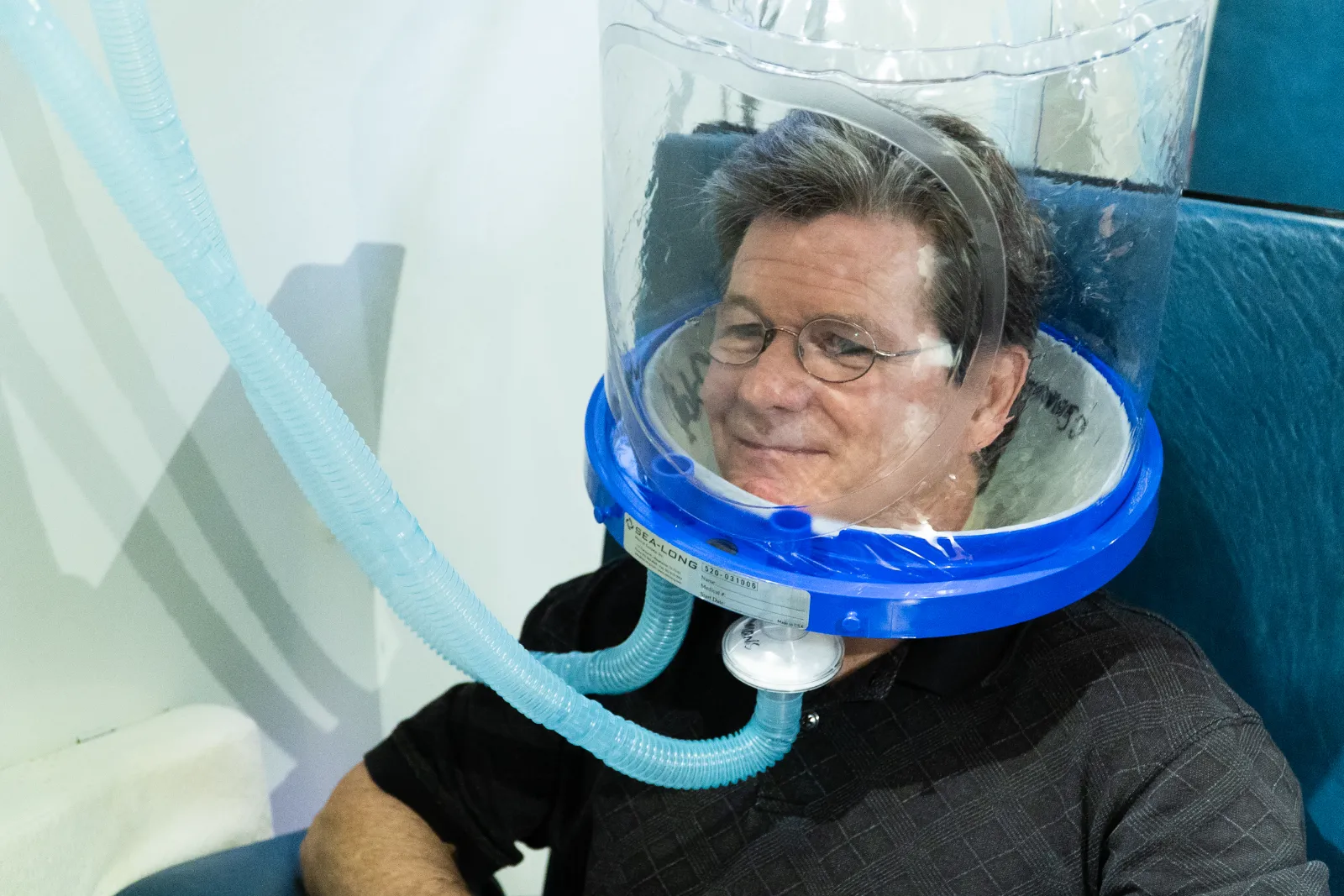
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) for Stroke
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) involves breathing 100% medical-grade oxygen inside a pressurized chamber, typically at 2.0 atmospheres absolute (ATA). This process greatly increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood plasma, enabling oxygen to reach areas of the brain and body that may have reduced blood flow after a stroke. By delivering oxygen more efficiently to damaged brain tissue, HBOT supports the body’s natural repair processes and helps create an environment where recovery is more likely.
Research suggests that HBOT may help improve neurological function, reduce brain swelling, and stimulate healing in the weeks and months following a stroke. While it is not a replacement for emergency care, it can serve as an effective adjunct therapy alongside standard stroke rehabilitation, potentially enhancing recovery outcomes.
How HBOT Supports Stroke Recovery
Supports Brain Tissue Repair
A stroke can leave areas of the brain starved for oxygen, slowing healing and limiting recovery. HBOT helps flood these tissues with oxygen, fueling cell metabolism, stimulating repair at the cellular level, and promoting the regeneration of healthy brain cells.

Reduces Brain Swelling and Inflammation
Following a stroke, inflammation can worsen neurological damage. HBOT helps reduce swelling by encouraging blood vessel constriction (vasoconstriction) while still delivering high levels of oxygen to the brain. This reduction in inflammation supports better recovery conditions and may help protect surrounding brain tissue.
Enhanced Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to form new connections—is essential during stroke recovery. By improving oxygen delivery to injured areas, HBOT may help the brain rewire itself, potentially improving movement, speech, memory, and other functions affected by the stroke.
Promotes Circulation and Blood Vessel Growth
HBOT promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is critical for restoring blood flow to brain regions affected by the stroke. Better circulation ensures that oxygen and nutrients reach healing tissues, supporting long-term recovery.

Improves Motor Function and Coordination
Stroke can disrupt the brain’s ability to control movement, leading to weakness, stiffness, or loss of coordination in certain muscles. By increasing oxygen delivery to brain regions involved in motor control, HBOT supports the repair of damaged neural pathways. This can help restore muscle strength, improve balance, and enhance coordination during stroke recovery.
Supports Immune Function and Cellular Health
Oxygen-rich environments strengthen immune cell performance and improve the body’s ability to repair and protect brain tissue. HBOT increases the activity and efficiency of white blood cells, enhancing their ability to fight infection, remove cellular debris, and regulate inflammation. This creates a cleaner, healthier environment for healing within the brain. By supporting overall cellular health, HBOT contributes to a stronger recovery foundation.
Neurofeedback Therapy for Stroke
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive brain training method that uses real-time monitoring of brainwave activity to help the brain learn how to self-regulate and function more efficiently. During a session, sensors placed on the scalp measure electrical activity in the brain, which is then displayed through visual or auditory cues—such as changes in a video, game, or sound. When brainwave activity moves toward healthier patterns, the feedback rewards the brain, reinforcing those changes over time. After a stroke, certain brain regions may become underactive, overactive, or disconnected from normal communication patterns. Neurofeedback provides the brain with instant feedback, encouraging it to form new, healthier patterns that support recovery and improve overall brain function.
How Neurofeedback Supports Stroke Recovery
Sharpens Cognitive Function
By training the brain to operate in more balanced patterns, neurofeedback can help improve attention, memory, and mental clarity—functions often affected after a stroke. Over time, these gains may support better problem-solving, faster information processing, and greater independence in daily activities.
Improves Emotional Regulation
Post-stroke changes in mood, such as anxiety, irritability, or depression, can make recovery more difficult. Neurofeedback helps stabilize brainwave activity, which may promote a calmer emotional state and greater resilience during rehabilitation.
Rebuild Movement Control
Neurofeedback can encourage stronger communication between brain regions responsible for movement, aiding in the recovery of fine motor skills, coordination, and balance after a stroke. This improved brain-to-body connection can make daily activities—such as walking, writing, or using utensils—feel more natural and controlled over time.
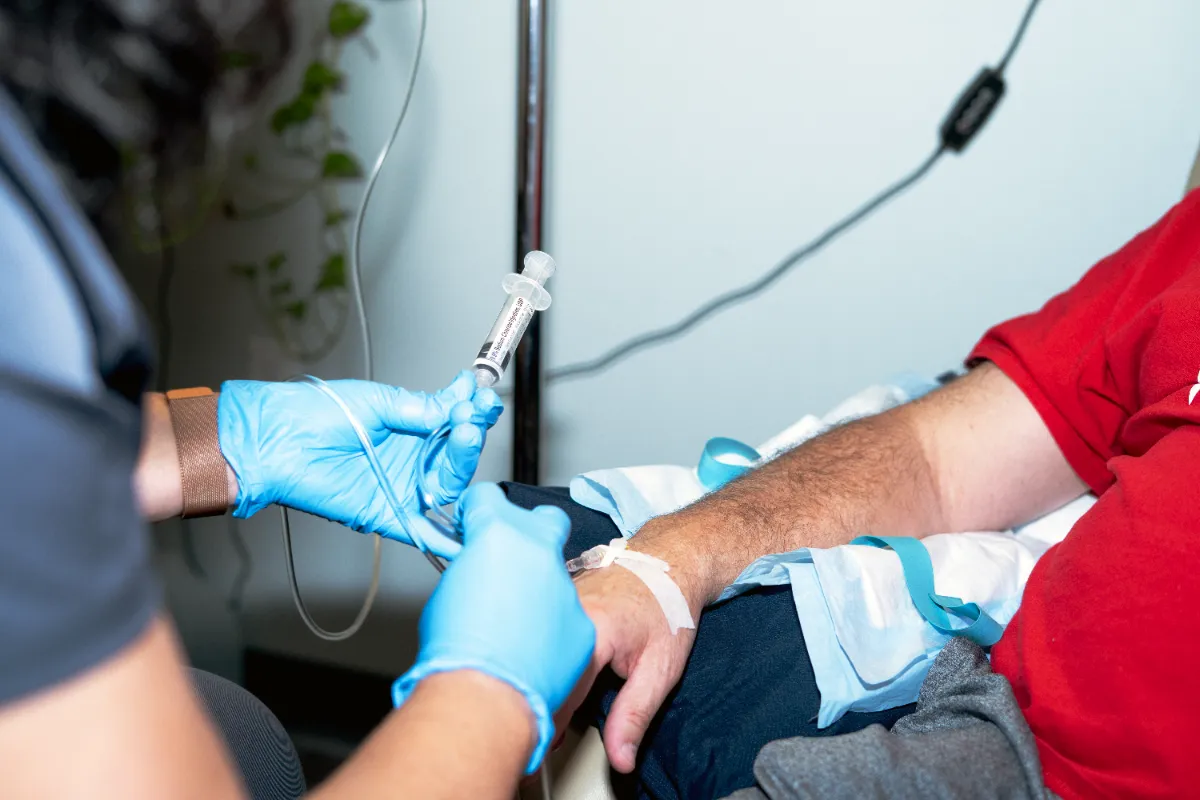
IV Therapy for Stroke
Nutritional IV Therapy delivers a precise blend of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants directly into the bloodstream—bypassing the digestive system for faster and more complete absorption. For individuals recovering from a stroke, this therapy can help restore nutrient levels, support brain and nervous system health, reduce inflammation, and improve cellular energy production. By delivering concentrated nutrients where they are needed most, IV Therapy can help boost energy, promote tissue repair, and create an internal environment that supports neurological healing and overall recovery.

How IV Therapy Supports Stroke Recovery
Boosts Brain and Nerve Health
After a stroke, the brain and nervous system require targeted nutrients to repair damaged cells and restore proper communication between neurons. IV Therapy delivers brain-supportive vitamins and minerals directly into circulation, helping to maintain nerve health, protect against oxidative stress, and promote neurological resilience.
Restores Vital Nutrients for Healing
Stroke recovery often involves lifestyle adjustments, medications, and physical rehabilitation that can deplete essential nutrients. IV Therapy replenishes key vitamins and minerals in a highly absorbable form, supporting energy production, tissue repair, and cognitive function.
Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can slow recovery and damage healthy brain tissue. IV Therapy provides anti-inflammatory nutrients and antioxidants that help protect cells, calm inflammation, and promote healing at the cellular level.
Key IV Recommendations for Stroke Recovery
Myers’ Cocktail IV
Components: B-complex vitamins, Vitamin C, Magnesium, Calcium, and Glutathione Push
- B12 and B-complex vitamins support energy production, nerve function, and cognitive clarity—critical for regaining brain and muscle performance after a stroke.
- Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant, helping to reduce oxidative stress, support immune function, and protect healthy brain tissue.
- Magnesium supports nerve transmission, muscle relaxation, and overall neurological balance, while calcium helps maintain muscle and bone strength during rehabilitation.
- Calcium supports nerve signaling and muscle function, which can aid physical recovery and reduce post-stroke cramping or spasms.
- Glutathione, often paired with the Myers’ Cocktail, is one of the body’s most important antioxidants. It helps neutralize harmful free radicals, protect brain cells from further damage, support mitochondrial function, reduce inflammation, and detoxify cells—creating a cleaner environment for brain repair.
NAD+ Trio IV
Components: NAD+, Reduced Glutathione, Myers’ Cocktail
- Targets multiple aspects of stroke recovery. Together, these components help reduce inflammation, promote nerve repair, restore nutrient balance, and create an optimal internal environment for brain healing after a stroke.
- NAD+ plays a key role in cellular energy production and mitochondrial function, which can help improve mental clarity, focus, and overall brain energy during stroke recovery.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy for Stroke
PEMF Therapy uses low-frequency, pulsing electromagnetic fields to help recharge cells, improve circulation, and support tissue repair. By increasing oxygen delivery, reducing inflammation, and boosting cellular energy, this non-invasive therapy can aid neurological healing during and after stroke recovery. PEMF may help reduce muscle stiffness, improve coordination, and create a more supportive environment for brain repair—making it a valuable complementary therapy alongside conventional stroke rehabilitation.
How PEMF Therapy Supports Stroke Recovery
Promotes Healing After Stroke
PEMF Therapy helps stimulate tissue repair in the brain and body while reducing swelling and improving blood flow. This can support faster recovery, enhance comfort, and aid in regaining function after a stroke
Calms Inflammation in the Brain and Body
Chronic inflammation after a stroke can interfere with brain repair and slow recovery. PEMF Therapy helps reduce inflammation at the cellular level, creating a healthier environment for neural regeneration and overall healing.
Energizes Cells for Better Function
PEMF Therapy improves mitochondrial function, increasing ATP production—the energy every cell needs to operate and repair itself. This energy boost supports brain cell recovery, enhances physical stamina, and may improve overall neurological performance during stroke rehabilitation.
Ready to Begin Your Journey to Recovery?
Schedule a free Personalized Wellness Visit to explore a custom plan today.
Schedule Your Free Wellness Visit →
References:
- Hadanny, Amir, Mor Rittblat, et al. “Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves neurocognitive functions of post-stroke patients – a retrospective analysis.” Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, vol. 38, no. 1, 21 Jan. 2020, pp. 93–107, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26078768/.
- Schmutz, Jörg, et al. “Hyperbaric oxygen in Post-Stroke Patients: A Feasibility Study.” Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, vol. 7, no. 4, 28 Nov. 2023, p. 41, https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7040041.
- Efrati, Shai, et al. “Hyperbaric oxygen induces late neuroplasticity in post stroke patients – randomized, prospective trial.” PLoS ONE, vol. 8, no. 1, 15 Jan. 2013, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053716.
- Nyam, Tee-Tau Eric, et al. “Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces the traumatic brain injury–mediated neuroinflammation through enrichment of prevotella copri in the gut of male rats.” Neurocritical Care, vol. 41, no. 3, 15 May 2024, pp. 798–812, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-024-01997-1.
- Buckley, Christopher J. “Hyperbaric Oxygen Effects on Angiogenesis.” StatPearls, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 4 Sept. 2023, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482485/.
- Renton, Tian, et al. “Neurofeedback as a form of cognitive rehabilitation therapy following stroke: A systematic review.” PLOS ONE, vol. 12, no. 5, 16 May 2017, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177290.
- Nan, Wenya, et al. “Neurofeedback training for cognitive and Motor Function Rehabilitation in chronic stroke: Two case reports.” Frontiers in Neurology, vol. 10, 24 July 2019, https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00800.
- Wang, Congxiao, et al. “Nicotinamide administration improves remyelination after stroke.” Neural Plasticity, vol. 2017, 1 June 2017, pp. 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7019803.
- Maksimova, Marina Yurievna, et al. “Impact of glutathione on acute ischemic stroke severity and outcome: Possible role of aminothiols redox status.” Redox Report, vol. 26, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2021, pp. 117–123, https://doi.org/10.1080/13510002.2021.1952819.
- Zhao, Binghao, et al. “The effect of magnesium intake on stroke incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis.” Frontiers in Neurology, vol. 10, 7 Aug. 2019, https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00852.
- Wang, Liping, et al. “Meta-analysis reveals protective effects of vitamin B on stroke patients.” Translational Neuroscience, vol. 6, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2015, pp. 150–156, https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2015-0014.
- Weisinger, Batsheva, et al. “Frequency-tuned electromagnetic field therapy improves post-stroke motor function: A pilot randomized controlled trial.” Frontiers in Neurology, vol. 13, 14 Nov. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.1004677.
- Capone, Fioravante, et al. “Pulsed electromagnetic fields: A novel attractive therapeutic opportunity for neuroprotection after acute cerebral ischemia.” Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface, vol. 25, no. 8, Dec. 2022, pp. 1240–1247, https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.13489.