Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is one of the most common and dangerous forms of accidental poisoning worldwide. This colorless, odorless gas is produced by burning fuels such as gas, wood, charcoal, or oil in poorly ventilated spaces. When inhaled, carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin in the blood far more effectively than oxygen, severely restricting the body’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues and organs.
Even brief exposure to high levels of CO can cause serious health consequences, including brain damage, heart complications, and in severe cases, death. Early symptoms can include headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and confusion—but the condition can escalate quickly without noticeable warning signs.
At Extivita, we provide evidence-based therapies designed to reduce long-term damage, improve oxygenation, and support full neurological recovery for individuals who have experienced CO poisoning.
Understanding Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning occurs when CO gas binds to hemoglobin more effectively than oxygen, severely reducing oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues. This results in hypoxia, cellular injury, and in severe cases, death. The brain and heart are especially vulnerable to oxygen deprivation, leading to neurological impairment, memory loss, and cardiovascular complications.
Prompt treatment is essential to reduce the risk of long-term brain damage, cognitive deficits, and organ dysfunction. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is the FDA-approved treatment for CO poisoning and can significantly enhance recovery when administered promptly.
Extivita Therapies for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy

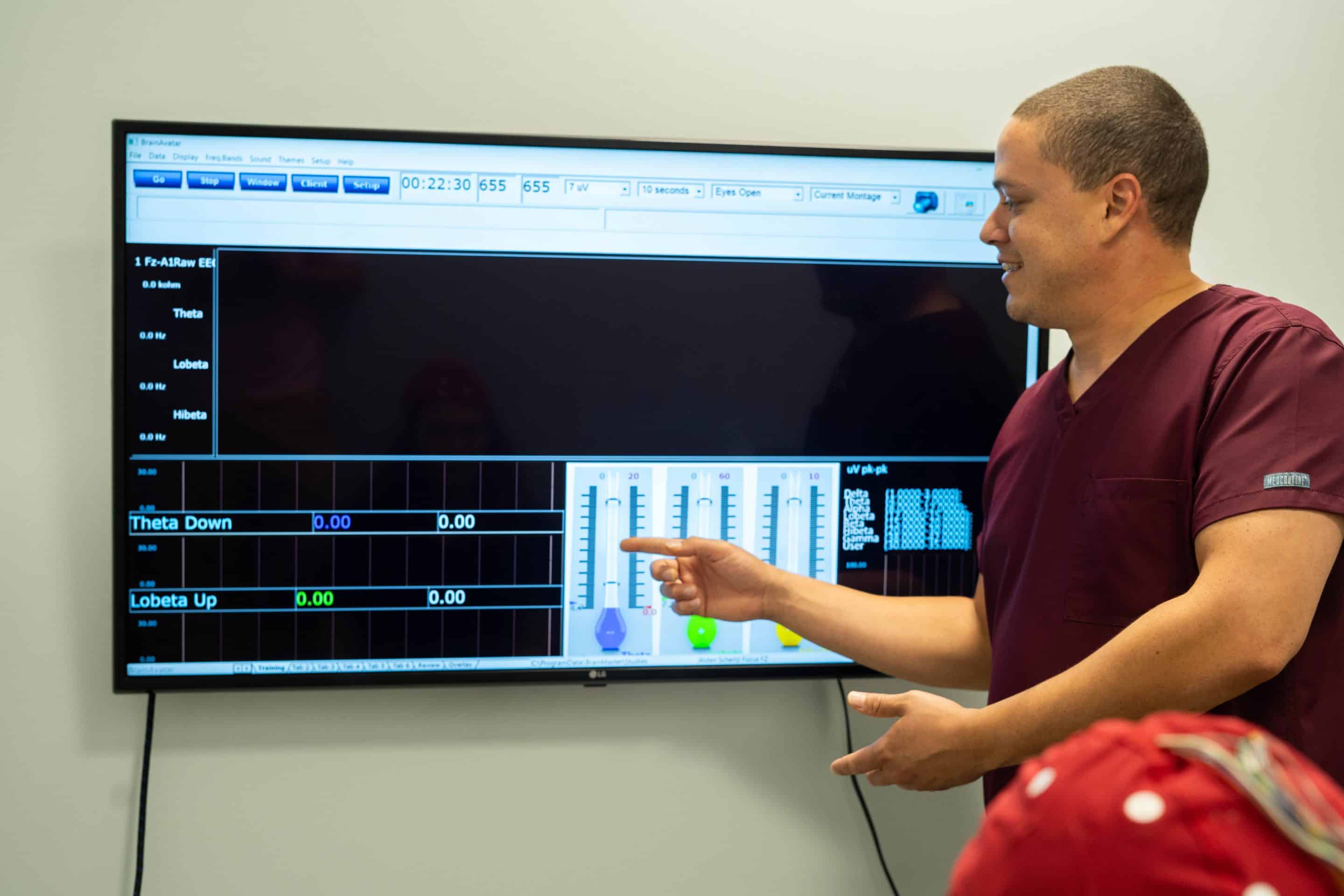
Neurofeedback

Nutritional IV Therapy

Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF)
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) for CO Poisoning Recovery
HBOT is the gold standard and FDA-approved treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning, particularly in cases of moderate to severe exposure or when neurological symptoms are present. The unique ability of HBOT to deliver high concentrations of oxygen under pressure provides several critical benefits.
Benefits for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Rapid Elimination of Carbon Monoxide
HBOT significantly reduces the half-life of carboxyhemoglobin (the compound formed when CO binds to hemoglobin) from about 5 hours (on room air) to approximately 20–30 minutes under hyperbaric conditions. This allows the body to quickly replace CO with oxygen in the bloodstream, restoring oxygen transport capacity to tissues.
Reoxygenation of Hypoxic Tissues
By dramatically increasing the amount of dissolved oxygen in plasma, HBOT ensures that oxygen is delivered directly to starved tissues—even where blood flow may be compromised. This is especially vital in:
- Brain tissue
- Heart muscle
- Organs sensitive to oxygen deprivation
Prevention of Delayed Neurological Sequelae (DNS)
One of the most serious risks of CO poisoning is the development of Delayed Neurological Sequelae, which can emerge days to weeks after initial exposure. Symptoms include:
- Memory loss
- Cognitive impairment
- Personality changes
- Balance and coordination issues
Studies have shown that HBOT reduces the incidence and severity of DNS, likely by:
- Reducing oxidative stress
- Minimizing lipid peroxidation in nerve tissues
- Protecting the blood-brain barrier from further damage
Reduction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
CO poisoning triggers a cascade of oxidative damage and inflammation. HBOT:
- Decreases pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α
- Enhances the body’s natural antioxidant defenses
- Improves mitochondrial function, supporting cellular repair
Neuroprotection and Support for Brain Healing
By improving oxygen delivery to the central nervous system, HBOT may help preserve neurological function and stimulate neuroplasticity, which aids recovery from:
- Brain fog
- Mood disturbances
- Coordination and motor deficits
- Headaches
Clinical Evidence
A landmark study by Weaver et al. (2002) demonstrated that patients who received HBOT after CO poisoning experienced significantly fewer neurocognitive deficits compared to those treated with normobaric oxygen alone.
Neurofeedback Therapy for CO
Poisoning Recovery
While Neurofeedback is not an acute treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning, it is a valuable adjunctive therapy for patients experiencing lingering cognitive, emotional, or neurological symptoms after exposure—especially in cases of Delayed Neurological Sequelae (DNS).
CO poisoning can lead to disruptions in brainwave activity, neuroinflammation, and impaired neural connectivity. Neurofeedback can help the brain retrain its electrical patterns, supporting recovery of normal function over time.
Neurofeedback Benefits
Restores Brainwave Balance and Function
CO poisoning can cause:
- Dysregulated brainwave activity
- Slower cognitive processing
- Difficulty with attention, memory, and focus
Through real-time feedback, neurofeedback training guides the brain to normalize brainwave patterns, which may help improve:
- Cognitive speed and clarity
- Focus and attention
- Working memory
Improves Emotional Regulation
Mood disturbances such as anxiety, irritability, depression, and mood swings are common in patients recovering from CO poisoning, particularly when the brain’s regulatory centers are affected.
Neurofeedback helps strengthen self-regulation of the brain’s emotional centers, potentially leading to:
- Reduced anxiety and irritability
- Improved emotional stability
- Better stress tolerance
Supports Neuroplasticity
Neurofeedback promotes neuroplasticity, or the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections after injury. For individuals who suffered hypoxic brain injury due to CO exposure, this is critical in:
- Re-establishing healthy neural pathways
- Enhancing cognitive resilience
- Supporting long-term recovery of brain function

Improves Sleep Quality
Sleep disturbances are a common aftereffect of CO poisoning and hypoxic injury. Neurofeedback has been shown to help:
- Normalize sleep architecture
- Improve sleep onset and quality
- Reduce insomnia symptoms
Better sleep supports overall brain recovery and improves daytime functioning.
When to Recommend Neurofeedback for CO Poisoning
- When a patient exhibits persistent cognitive deficits, brain fog, or mood instability following acute CO poisoning treatment.
- For patients diagnosed with or showing signs of Delayed Neurological Sequelae (DNS).
- As part of a comprehensive neurological recovery plan that includes HBOT, IV therapy, and lifestyle support.
Clinical Insight
While specific large-scale studies on neurofeedback for CO poisoning are limited, research on neurofeedback for hypoxic brain injuries, PTSD, and neurocognitive disorders supports its use as a recovery tool for enhancing brain regulation and function.
IV Therapy for CO Poisoning Recovery
When nutrients are delivered intravenously (through an IV), nearly 100% of those nutrients are immediately available to your cells and tissues via the bloodstream. This bypasses the digestive system, allowing for faster and more complete absorption than oral supplements can provide. IV therapy ensures that essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants reach your brain and body quickly, which is especially beneficial during neurological recovery when nutrient demand is elevated.

While IV Nutrient Therapy is not a primary treatment for acute CO poisoning, it can play a significant supportive role in recovery, particularly for addressing:
- Oxidative stress
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Persistent fatigue
- Neurological symptoms
- Immune dysregulation
IV therapy delivers targeted nutrients directly into the bloodstream for immediate absorption, bypassing the digestive system and enhancing cellular uptake.
Research shows how IV Therapy
Enhances Mitochondrial Function and Cellular Energy
CO poisoning impairs the body’s ability to utilize oxygen, which can disrupt mitochondrial energy production (ATP synthesis). IV therapies that include:
- B-Complex Vitamins (especially B1, B6, B12)
- NAD+ – A coenzyme critical for energy metabolism and cellular repair
- Magnesium – Supports nerve function and ATP production
These nutrients help restore mitochondrial function, leading to improved energy, reduced fatigue, and better cognitive performance.
Supports Neurological Recovery
Neurotoxicity from CO exposure can lead to delayed cognitive impairment, mood changes, and memory deficits. IV nutrients such as:
- B vitamins (especially B12 and Folate) – Essential for nerve regeneration and neurotransmitter synthesis
- NAD+ – Supports neuronal repair and enhances neuroplasticity
- Glutathione – Reduces inflammation in neural tissues
This combination may help reduce brain fog, improve mental clarity, and support mood stability.
Boosts Immune Function
After CO poisoning, the body’s immune system may be compromised, increasing vulnerability to infections or prolonged inflammatory states. High-dose Vitamin C, delivered via IV, can:
- Strengthen immune defenses
- Promote tissue repair
- Shorten recovery time
Recommended IV Protocols for CO Poisoning Recovery:
Myers’ Cocktail IV
A foundational blend of vitamins and minerals for general recovery
Components: B-complex vitamins, Vitamin C, Magnesium, and Calcium
- B-complex vitamins and magnesium are essential for nerve repair and neurotransmitter balance, both of which
are often disrupted after a brain injury. - Vitamin C and calcium contribute to antioxidant defense and metabolic support. They also help combat oxidative
stress and support cellular healing in the brain, contributing to overall neurological recovery.
Glutathione Push
Administered after the Myers’ for detox and antioxidant support
Vitamin C High Dose Infusion
For antioxidant and immune support
NAD+ Trio IV
For cellular and cognitive restoration
Components: NAD+, Glutathione, and Magnesium
- NAD+ plays a key role in cellular energy production and may help improve cognitive function, focus, and mental
clarity after injury. - Glutathione helps reduce neuroinflammation and supports detoxification at the cellular level.
- Magnesium promotes calming brainwave activity and supports healthy neurological signaling.
Clinical Insight
While there are no large-scale studies specific to IV therapy for CO poisoning, the components of these infusions are well-researched for:
- Oxidative stress reduction
- Neurological repair
- Mitochondrial health
These therapies are commonly used in functional medicine for post-toxic exposure recovery.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy for CO Poisoning Recovery
PEMF Therapy uses low-frequency electromagnetic pulses to gently stimulate the body’s cells. This non-invasive treatment enhances circulation, supports cellular energy production, and promotes tissue repair—key components in neurological recovery after brain injury.
While PEMF Therapy is not a primary treatment for acute CO poisoning, it offers complementary support during the recovery phase, especially for individuals experiencing persistent neurological, vascular, or musculoskeletal symptoms after CO exposure.
How PEMF Therapy Supports CO Poisoning Recovery
Enhances Microcirculation and Oxygen Delivery
CO poisoning impairs tissue oxygenation by displacing oxygen from hemoglobin and reducing blood flow to critical tissues. PEMF has been shown to:
- Increase capillary blood flow
- Promote angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation)
- Improve tissue oxygenation and nutrient delivery
This can be particularly beneficial for brain and cardiac tissues that suffered hypoxic damage during CO poisoning.

Reduces Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:
CO poisoning triggers widespread oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. PEMF therapy can:
- Modulate the inflammatory response by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6
- Enhance antioxidant defenses at the cellular level
- Support the body’s detoxification pathways
This systemic anti-inflammatory effect can help mitigate lingering inflammation that contributes to Delayed Neurological Sequelae (DNS) or cognitive dysfunction.
Supports Neurological Recovery and Nerve Repair:
PEMF therapy has demonstrated potential in:
- Stimulating nerve regeneration
- Enhancing neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to rewire and repair)
- Promoting myelin repair and protecting nerve cells from further oxidative damage
This makes PEMF a valuable adjunct for patients experiencing neuropathy, brain fog, or neurocognitive deficits post-CO poisoning.

Improves Cellular Energy and Mitochondrial Function:
By influencing ion exchange across cell membranes, PEMF supports:
- Increased ATP (cellular energy) production
- Improved mitochondrial efficiency
- Faster cellular repair and regeneration
This is essential for energy restoration and overall recovery, particularly for patients with fatigue, weakness, or exercise intolerance post-exposure.
When to Recommend PEMF for CO Poisoning
- During the sub-acute or recovery phase, after stabilization and primary HBOT treatment
- For patients with ongoing:
- Cognitive dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Neuropathy or nerve pain
- Circulation issues
- As part of a comprehensive neurological recovery plan
Supporting Research
While direct studies on PEMF for CO poisoning are limited, studies on PEMF’s benefits for:
- Neuroregeneration
- Chronic inflammation reduction
- Microcirculation improvement
…support its adjunctive use in hypoxic injuries and related conditions.
Schedule a free wellness consultation to explore a personalized plan that supports your cognitive health and overall brain function.
Schedule Your Free Wellness Visit →
References:
- Weaver, L.K., Hopkins, R.O., Chan, K.J., et al. (2002). Hyperbaric oxygen for acute carbon monoxide poisoning. New England Journal of Medicine, 347(14), 1057–1067. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa013121
- Thom, S.R. (2011). Hyperbaric oxygen: its mechanisms and efficacy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 127(1 Suppl), 131S–141S. DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181fbe2bf
- Harch, P.G., et al. (2015). Hyperbaric oxygen can induce neuroplasticity and improve cognitive functions of patients suffering from anoxic brain damage. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 33(4), 471–486. DOI: 10.3233/RNN-150517
- Thom, S.R., Bhopale, V.M., Velazquez, O.C., Goldstein, L.J., Thom, L.H. (2006). Stem cell mobilization by hyperbaric oxygen. American Journal of Physiology – Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 290(4), H1378–H1386. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00888.2005
- Wu, F., et al. (2019). Vitamin B12 enhances nerve repair and improves functional recovery after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting ER stress-induced neuron injury. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 406. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00406
- Linseman, D.A., & Koza, L. (2019). Glutathione precursors shield the brain from trauma. Neural Regeneration Research, 14(10), 1701. DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.257520
- Patchana, T., et al. (2023). Immunomodulatory effect of electromagnetic field in the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Journal of Biotechnology and Biomedicine, 6(1), 1-10. DOI: 10.26502/jbb.2642-91280069
- Miller, C.P., et al. (2020). Transcranial low‐frequency pulsating electromagnetic fields (t‐pemf) as post‐concussion syndrome treatment. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 142(6), 597-604. DOI: 10.1111/ane.13300