Burns
Burns are serious injuries that can affect more than just the skin. When someone suffers a moderate or severe burn, it can lead to problems like pain, swelling, slow healing, and even infections. These injuries can also cause stress on the entire body, making it harder to recover and regain energy. When the skin is damaged, the body works hard to repair it—but the healing process can be slow. Burns often reduce oxygen in the injured area, which is needed for skin and tissue to heal properly. They also cause inflammation and stress in the body, which can make things worse over time.
These challenges make it important to support the body’s natural healing systems. At Extivita, we take an integrative, whole-body approach to burn recovery—one that focuses on restoring oxygen flow, reducing inflammation, enhancing circulation, and promoting faster tissue repair. With the combination of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), Nutritional IV Therapy, and PEMF Therapy, our goal is to help your body heal more quickly, reduce inflammation, and reduce the long-term effects of burn injuries.
Our Integrative Approach
At Extivita, we offer a comprehensive, science-backed approach to support the body’s natural healing process after burn injuries. Our therapies—including Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), Nutritional IV Therapy, and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy—are designed to work together to accelerate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, restore hydration and nutrient levels, and promote optimal recovery. By addressing both the surface injury and the body’s internal healing systems, we help patients recover faster, more comfortably, and more completely.
Extivita Therapies for Burns

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy

Nutritional IV Therapy

Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy (PEMF)
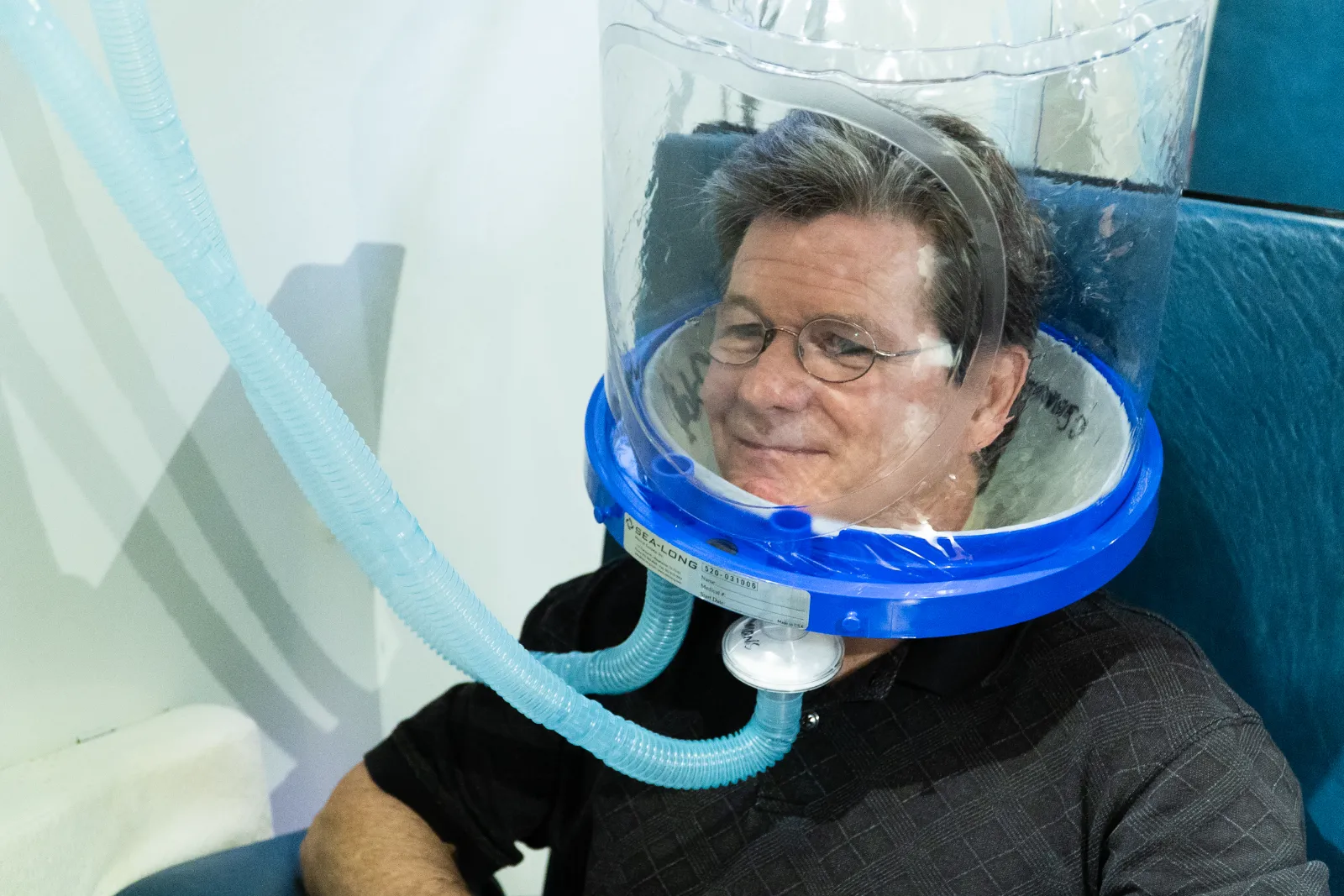
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) for Burns
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) involves breathing 100% medical-grade oxygen inside a pressurized chamber, typically at 2.0 atmospheres absolute (ATA). This process increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood plasma, allowing oxygen to reach damaged tissues that may have limited blood flow due to the injury. For burn patients, this increased oxygen delivery accelerates healing, reduces swelling, enhances immune response, and supports tissue regeneration.
HBOT is widely recognized as an effective adjunct therapy for moderate to severe burns and can significantly improve outcomes when added to standard wound care.
Burn Recovery Benefits
Accelerates Wound Healing
Burns disrupt skin and tissue structure, slowing the body’s ability to repair itself. HBOT boosts the supply of oxygen to the burn site, which fuels the body’s natural healing processes. This increased oxygen helps regenerate tissue, stimulate the growth of new skin cells, and repair blood vessels—all critical for fast and complete healing.

Reduces Inflammation and Swelling
Severe burns trigger a widespread inflammatory response, which can worsen tissue damage. HBOT helps reduce this inflammation by constricting blood vessels (vasoconstriction) and limiting fluid buildup in the affected areas. This not only eases pain and pressure but also supports a healthier healing environment.
Fights Infection
Burn wounds are highly vulnerable to infection, which can delay healing and lead to complications. HBOT strengthens the immune system’s response by boosting the effectiveness of white blood cells and increasing oxygen levels in tissues—making it harder for bacteria to survive. This can lower the need for antibiotics and reduce the risk of sepsis.
Improves Circulation and Blood Vessel Growth
HBOT promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. This is vital for delivering nutrients and oxygen to burned areas with compromised blood flow. Better circulation ensures faster healing and helps restore function to damaged tissues.
Minimizes Scarring
By enhancing oxygen supply during the early stages of wound healing, HBOT may reduce the severity of scarring. Faster tissue repair with less inflammation helps the skin regenerate more evenly, improving cosmetic outcomes and mobility—especially for burns affecting joints or facial areas.
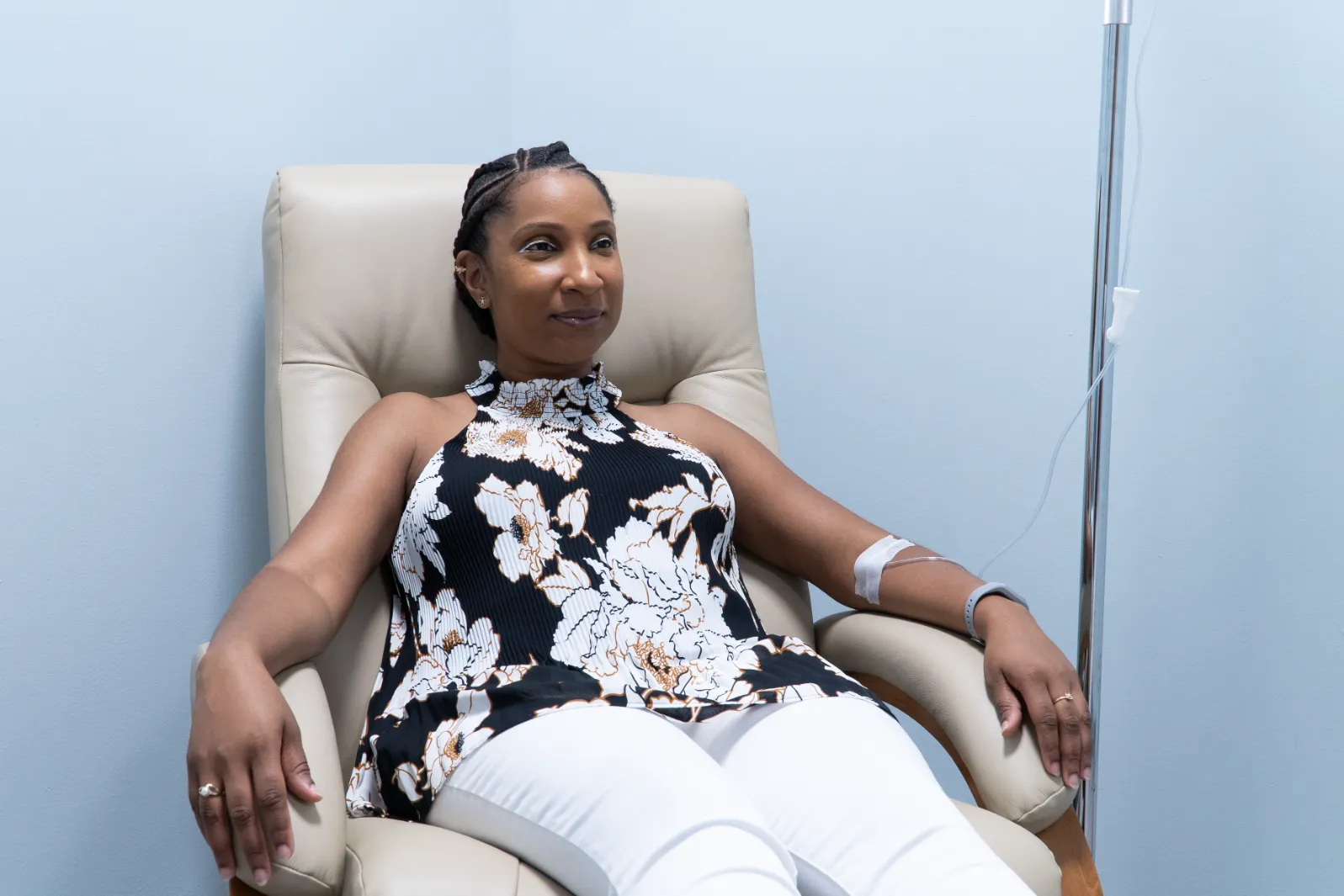
IV Therapy for Burns
Nutritional IV Therapy delivers a powerful blend of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and electrolytes directly into your bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system for optimal absorption. For individuals recovering from burn injuries, this therapy plays a vital role in accelerating wound healing, reducing inflammation, restoring hydration, and strengthening the immune system—all critical for a smooth and complete recovery process.

How IV Therapy Helps with Burns
Replenishes Nutrient Losses
Burn injuries rapidly deplete the body of essential nutrients such as vitamin C, magnesium, B-complex vitamins, and trace minerals. IV Therapy restores these key nutrients to support energy production, immune function, and cellular repair—helping patients recover faster and more comfortably.
Enhances Tissue Repair and Collagen Formation
High-dose vitamin C delivered intravenously promotes collagen synthesis, speeds up skin regeneration, and strengthens connective tissue. These effects are essential for healing damaged skin and reducing scar formation after burns.
Regulates Fluid Balance and Electrolyte Function
Burns lead to significant fluid loss through damaged skin. Nutrients like potassium and magnesium help regulate fluid distribution, support organ function, and prevent dehydration and fatigue—ensuring optimal recovery and stability.

Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Antioxidants such as glutathione neutralize free radicals produced by burn trauma. This reduces systemic inflammation, supports detoxification, and protects tissues from further damage, creating a more favorable environment for healing.
Key IV Recommendations for Burn Recovery
Myers’ Cocktail IV
Components: B-complex vitamins, Vitamin C, Magnesium, and Calcium
- Vitamin C supports collagen synthesis, which is essential for skin regeneration and proper wound healing.
- B-complex vitamins help the body produce energy at the cellular level and assist in tissue repair.
- Magnesium plays a key role in reducing inflammation and easing muscle tension.
- Calcium is important for healthy nerve signaling and contributes to effective tissue regeneration.
Glutathione IV
Components: Reduced Glutathione
- It neutralizes free radicals that are produced in large amounts after burn injuries.
- It supports liver detoxification, helping the body process and eliminate toxins more efficiently.
- It reduces systemic inflammation, which can speed up healing and improve comfort.
Hydration IV
Components: Normal Saline
-
It helps maintain healthy blood volume and supports proper circulation to damaged tissues.
-
It prevents dehydration and reduces fatigue, both common issues in burn recovery.
-
It supports overall organ function by replenishing lost fluids and electrolytes.
High-Dose Vitamin C IV
Components: Vitamin C, Magnesium, Calcium and Potassium
-
High doses of Vitamin C reduces oxidative stress caused by burn trauma, helping to protect tissues from further damage.
-
It supports the immune system, making it easier for the body to fight off infection during recovery.
-
Potassium, included in this IV, helps regulate fluid distribution in the body—crucial for burn recovery when fluid
shifts and losses are common.
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy for Burns
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Therapy uses low-frequency electromagnetic waves to stimulate cellular repair and improve circulation. For burn injuries, this non-invasive therapy supports the body’s natural healing processes by reducing pain, inflammation, and tissue damage. PEMF helps recharge damaged cells, making it easier for the body to heal from the inside out.
How PEMF Therapy Supports Burn Recovery

Reduces Joint Pain and Inflammation
Burns often cause lingering pain and swelling. PEMF Therapy helps calm inflammation and decrease pain by improving blood flow and restoring balance to overactive nerve cells—helping you feel more comfortable during recovery.
Accelerates Tissue Repair
PEMF stimulates the production of ATP (the body’s energy source), which gives cells the fuel they need to regenerate skin and heal wounds. This can lead to faster recovery and improved skin quality in the healing area.
Circulation and Oxygen Delivery
Healthy blood flow is essential for burn healing. PEMF encourages better circulation, which helps bring more oxygen and nutrients to the affected areas—supporting deeper, more complete healing.
Minimizes Scar Tissue Formation
By supporting a healthy healing process and reducing inflammation early on, PEMF may help minimize thick or raised scarring. This can improve long-term mobility and cosmetic outcomes, especially in areas like the face or joints.
Read to Begin Your Journey to Recovery?
Schedule a free Personalized Wellness Visit to explore a custom plan today.
Schedule Your Free Wellness Visit →
References:
- Niinikoski, Juha H.A. “Clinical hyperbaric oxygen therapy, wound perfusion, and transcutaneous oximetry.” World Journal of Surgery, vol. 28, no. 3, 17 Feb. 2004, pp. 307–311, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-003-7401-1.
- Oley, Mendy Hatibie, et al. “Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on the healing of thermal burns and its relationship with ICAM-1: A case-control study.” Annals of Medicine and Surgery, vol. 61, Jan. 2021, pp. 104–109, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2020.12.025.
- Bhutani, Sourabh, and Guruswamy Vishwanath. “Hyperbaric oxygen and wound healing.” Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, vol. 45, no. 02, May 2012, pp. 316–324, https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-0358.101309.
- Hatibie, Mendy J., et al. “Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for second-Degree Burn Healing: An experimental study in Rabbits.” Advances in Skin & Wound Care, vol. 32, no. 3, Mar. 2019, pp. 1–4, https://doi.org/10.1097/01.asw.0000553110.78375.7b.
- Subramaniam, Thayaalini, et al. “The role of calcium in wound healing.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 22, no. 12, 17 June 2021, p. 6486, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126486.
- Malkoc, Aldin, et al. “High-dose intravenous versus low-dose oral vitamin C in burn care: Potential protective effects in the severely burned: A retrospective cohort study.” Annals of Medicine & Surgery, vol. 85, no. 5, 11 Apr. 2023, pp. 1523–1526, https://doi.org/10.1097/ms9.0000000000000615.
- Buz, A., et al. “Efficacy of glutathione Mesotherapy in Burns: An experimental study.” European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, vol. 42, no. 6, 27 Nov. 2015, pp. 775–783, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-015-0607-8.
- Nakajima, M., Kojiro, M., Aso, S. et al. Effect of high-dose vitamin C therapy on severe burn patients: a nationwide cohort study. Crit Care 23, 407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-019-2693-1
- Navarrete, Norberto. “Hyperkalemia in electrical burns: A retrospective study in Colombia.” Burns, vol. 44, no. 4, June 2018, pp. 941–946, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2017.12.003.
- Hinton, Pamela, et al. “Electrolyte changes after burn injury and effect of treatment.” The Lancet, vol. 302, no. 7823, Aug. 1973, pp. 218–221, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93129-2.
- Tabakan, Ibrahim, et al. “The healing effect of pulsed magnetic field on Burn wounds.” Burns, vol. 48, no. 3, May 2022, pp. 649–653, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2021.06.001.
- Keskin, Yaşar. “The effect of magnetic field therapy and electric stimulation on experimental burn healing.” Turkish Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, vol. 65, no. 4, 5 Dec. 2019, pp. 352–360, https://doi.org/10.5606/tftrd.2019.2899.