Boost Immunity
The immune system is an incredibly complex network of cells, collectively called white blood cells (WBCs), that protect the body from foreign substances. We cannot live without it. The immune system is found throughout the body: in the skin, lymph nodes, blood, tissues, and gastrointestinal system. When this system is weak, the body becomes increasingly susceptible to damage from pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites(1). Keeping your immune system strong is vital to lowering your risk of infection from something as common as a cold, a cut, or something bad you ate, to life-threatening viruses like Ebola and COVID-19.
Extivita Therapies to Boost Immunity:
Extivita Therapies to Boost Your Immunity:

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy

Supplements

Nutritional IV Therapy

Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Boost Immunity:

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) strengthens both the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. By doing so, the body is better prepared to eliminate pathogens before they can cause serious damage. HBOT improves the immune system through two main mechanisms. Firstly, HBOT increases the activity and efficacy of white blood cells (WBCs)(2, 3). WBCs are directly responsible for eliminating pathogens, so enhancing WBC activation results in a more effective immune response.
Secondly, HBOT floods tissues with oxygen, creating an environment in which harmful anaerobic bacteria (bacteria that live in low/no oxygen) cannot survive(4). Together, these mechanisms make HBOT an effective therapy for strengthening the immune system and decreasing risk of infection and pathogen-driven disease.
Effects of HBOT on Stroke:

Decreased Inflammation

New Blood Vessel Formation
Increased Stem Cell Activity
IV Therapy to Boost Immunity:
IV therapy, especially the Myer’s IV Cocktail, can provide an immediate boost to your immune system. Because IV infusions bypass the gastrointestinal system, 100% of the nutrients are delivered directly into the bloodstream, which is not the case with oral supplementation. This provides your cells with abundant doses of nutrients that enhance your cell’s ability to heal and perform other vital functions. The Myers’ IV Cocktail is a very effective treatment to boost the immune system because it delivers extra Vitamin C directly to your cells. Vitamin C reduces damaging free radicals and plays a significant role in immune cell functions such as phagocytosis (killing bacteria) and microbial destruction(7). Additionally, vitamin C can help shorten the duration of an existing infection(8).
Learn more about IV Therapy…

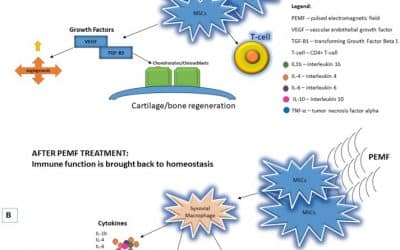
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy to Boost Immunity:
Pulse electromagnetic frequency therapy (PEMF) helps boost the immune system through multiple different mechanisms. Firstly, PEMF increases microcirculation, which refers to the blood flow in your capillaries. Your capillaries are the site of exchange between your blood and tissues, so optimal microcirculation ensures that your tissues receive everything they need to function optimally. This is also where white blood cells (WBCs), your immune cells, get transported from your blood to any tissues that require an immune response. By increasing microcirculation with PEMF, you increase WBC delivery to tissues and improve your body’s ability to respond to harmful pathogens. Secondly, PEMF has been shown to enhance the immune system by decreasing production of proinflammatory molecules and stabilizing/increasing anti-inflammatory molecule production(9).
Learn more about PEMF Therapy…
Recent Immunity News & Research:
Overview of the Immune System
Function The overall function of the immune system is to prevent or limit infection. An example of this principle is found in immune-compromised people, including those with genetic immune disorders, immune-debilitating infections like HIV, and even pregnant women,...
The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field to Modulate Inflammation and Improve Tissue Regeneration: A Review
[The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field to Modulate Inflammation and Improve Tissue Regeneration: A Review has been redirected to the below by PubMed] Targeting Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/Pericytes (MSCs) With Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Has the Potential to...
Hypoxia and hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a review
Abstract: Hypoxia causes a cascade of activity from the level of the individual down to the regulation and function of the cell nucleus. Prolonged periods of low oxygen tension are a core feature of several disease states. Advances in the study of molecular biology...
References
- Overview of the Immune System | NIH: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. http://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/immune-system-overview. Accessed 19 Nov. 2020.
- Struzyna, Jerzy, et al. “Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy of Burns.” Polski Przeglad Chirurgiczny/ Polish Journal of Surgery, vol. 80, Aug. 2008, pp. 423–30. ResearchGate, doi:10.2478/v10035-008-0060-z.
- Bitterman, N., et al. “Effect of a Single Exposure to Hyperbaric Oxygen on Blood Mononuclear Cells in Human Subjects.” Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine: Journal of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, Inc, vol. 20, no. 3, Sept. 1993, pp. 197–204.
- Vatansever, Fatma, et al. “Antimicrobial Strategies Centered around Reactive Oxygen Species – Bactericidal Antibiotics, Photodynamic Therapy, and Beyond.” FEMS Microbiology Reviews, vol. 37, no. 6, Nov. 2013, pp. 955–89, doi:10.1111/1574-6976.12026.
- Choudhury, Ryan. “Hypoxia and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Review.” International Journal of General Medicine, vol. 11, Nov. 2018, pp. 431–42. PubMed Central, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S172460.
- Devaraj, Divya, and D. Srisakthi. “Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy – Can It Be the New Era in Dentistry?” Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research: JCDR, vol. 8, no. 2, Feb. 2014, pp. 263–65. PubMed, doi:10.7860/JCDR/2014/7262.4077.
- Carr, Anitra C., and Silvia Maggini. “Vitamin C and Immune Function.” Nutrients, vol. 9, no. 11, Nov. 2017. PubMed Central, doi:10.3390/nu9111211.
- Hemilä, Harri, and Elizabeth Chalker. “Vitamin C for Preventing and Treating the Common Cold.” The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, no. 1, Jan. 2013, p. CD000980. PubMed, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4.
- Ross, Christina L., et al. “The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field to Modulate Inflammation and Improve Tissue Regeneration: A Review.” Bioelectricity, vol. 1, no. 4, Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers, Dec. 2019, pp. 247–59. liebertpub.com (Atypon), doi:10.1089/bioe.2019.0026.