Cancer treatments can be physically demanding, but innovative therapies like Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) and High-dose vitamin C IV offer new ways to enhance patient outcomes. These therapies, when used alongside conventional treatments, improve the body’s...
Vitamin C
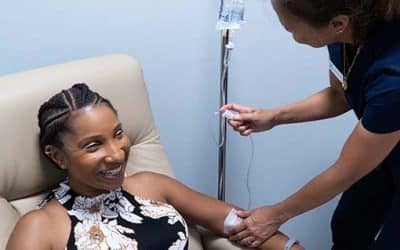
Cancer Treatment: Non-invasive High Dose Vitamin C IV Therapy
High-dose intravenous vitamin C (IVC) therapy, offered at Extivita, is an innovative approach in cancer treatment, complemented by Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy. This multifaceted approach aims to enhance overall...
Vitamin C function in the brain: vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2
Abstract: Ascorbate (vitamin C) is a vital antioxidant molecule in the brain. However, it also has a number of other important functions, participating as a cofactor in several enzyme reactions, including catecholamine synthesis, collagen production, and regulation of...
Ascorbic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice
Abstract Ascorbic acid (AA) has been shown to exert beneficial effects, including mitigating oxidative stress and inhibiting inflammation. However, the preventative effect of vitamin C in chronic inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) remains...
Effect of vitamin C on inflammation and metabolic markers in hypertensive and/or diabetic obese adults: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract Background: Obesity is well associated as being an interfering factor in metabolic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes by increasing the secretion of proinflammatory markers from adipose tissue. Having healthy effects, vitamin C could work as an...
Vitamin C and asthma
Abstract <no abstract to show> Hemilä, Harri. (2014). Vitamin C and asthma. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. 134. 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.032.
[Vitamin C and its physiological role with respect to the components of the immune system]
Abstract Vitamin C is a water soluble micronutrient commonly found in our diet which orchestrates the function of both innate and adaptive immune system, influencing both cellular and humoral immune responses. Vitamin C inhibits excessive activation of the immune...
Effects of high-dose B vitamin complex with vitamin C and minerals on subjective mood and performance in healthy males
Abstract Rationale: A significant proportion of the general population report supplementing their diet with one or more vitamins or minerals, with common reasons for doing so being to combat stress and fatigue and to improve mental functioning. Few studies have...
Associations of vitamin C status, fruit and vegetable intakes, and markers of inflammation and hemostasis
Abstract Background: It has been suggested that a high dietary intake and high circulating concentrations of vitamin C may protect against ischemic heart disease. Objectives: The objective was to examine the associations between dietary and plasma vitamin C...






![[Vitamin C and its physiological role with respect to the components of the immune system]](https://www.extivita.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/smoothies-2253423_1280-400x250.jpg)
